> ENC Master > Climate Encyclopaedia > Clouds & Particles > basics > 1. Clouds > - Formation of clouds
> ENC Master > Climate Encyclopaedia > Clouds & Particles > basics > 1. Clouds > - Formation of clouds
 |
|
|
|
Clouds & ParticlesBasics |
Formation of cloudsA cloud is composed of millions of little droplets of water (or ice crytals when temperature is very low) suspended in the air. Hence a cloud can form when water vapor becomes liquid, i.e. when the humid air is cooled and condenses on tiny particles. There are several major processes for cloud formation. |
|
Convection :On Earth, because of air density depending on temperature, the warm air rises and the cold air sinks as warm air is less dense than cold air. That is what scientists call convection.
|
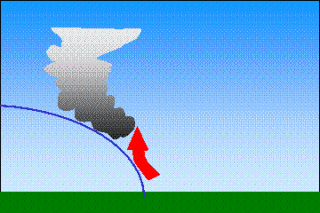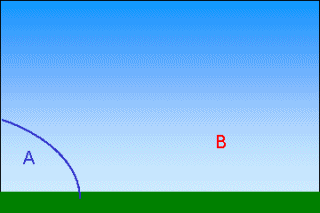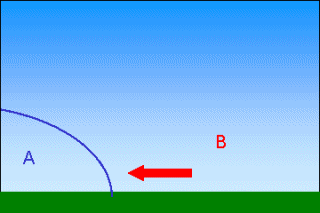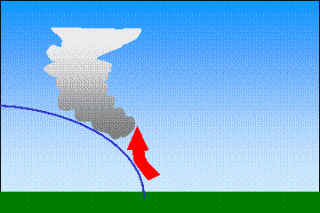
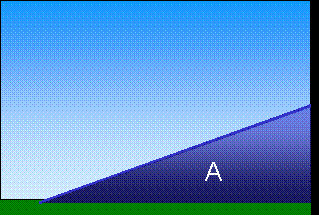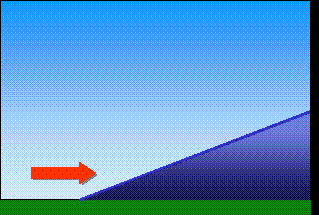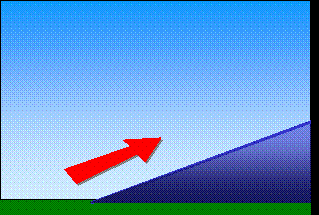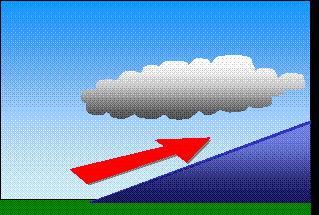
Topography (mountains)Clouds can also form because of the Earth's surface topography, mountains or hills for example. They are then called "orographic clouds".The air is forced to move over the mountain, and as it ascends, the air cools. If it cools to it's saturation point, condensation occurs and the water contained within the air becomes visible as a cloud.
|
|
|
|
The Foehn effect When air rises over the mountains, it cools and becomes saturated with water vapour. Condensation occurs and the water vapour becomes liquid. It stays under the form of a cloud or rains, while the air continues to rise. When the air mass descends on the other side of the mountain, it is more dry and warm. This difference in temperature is known as the Foehn effect. |
Meeting of air massesNot only mountains can force air to rise : when warm air meets a mass of heavier cold air, it is also forced to rise. The boundary between warm and cool air is called a « front ». As the warm air ascends it cools, and then clouds may be formed.
|
|
|
Horizontal motionSometimes winds bring warm and moist air into a region. If the warm moist air flows over a much colder surface, it is cooled and moisture will condense and form fog. This mechanism is frequent on the coast of continents. |
|
About this page... |