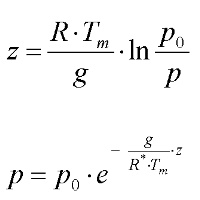> ENC Master > Climate Encyclopaedia > Upper Atmosphere > basics > 1. Understanding the stratosphere > pressure & altitude
> ENC Master > Climate Encyclopaedia > Upper Atmosphere > basics > 1. Understanding the stratosphere > pressure & altitude
Calculation of the relationship between atmospheric pressure and altitude for dry airparameters and units: z [m] = altitude p0 [hPa] = pressure at the ground p [hPa] = pressure at altitude z R* = 287 J kg-1 K-1 = gas constant for dry air R* = R / Ma R = gas constant = 8.314 J K-1 mol-1 Ma = molecular weight of air = 28.96 g mol-1 |
|
g = gravity accelaration constant Tm [K] = mid temperature between the the temperature at the ground T0 and the temperature in altitude z Tz Tm = (T0 + Tz) / 2 g / R* = 0.034 K m-1
|
1 J = 1 N m 1 N = 1 kg m s-2
|
|
|
|
The formula is only valid for dry air. For humid air the molecular weight changes. Temperature at the ground: 20°C Pressure at the ground: 1000 hPa It can be seen from the calculated pressures in higher altitudes, that the pressure in 5,500 m is about 500 hPa in 11,000 m about 250 hPa.
|
about this page:author: Dr. Elmar Uherek - Max Planck Institute, Mainz
|