> ENC Master > Climate Encyclopaedia > Clouds & Particles > more > 3. Clouds, particles and climate > - Radiation budget
> ENC Master > Climate Encyclopaedia > Clouds & Particles > more > 3. Clouds, particles and climate > - Radiation budget
 |
|
|
|
Clouds & ParticlesMore |
Radiation budgetRadiation budget is the balance between incoming energy from the Sun and outgoing energy from the Earth. This energy can be directly reflected towards space by the Earth, with the help of clouds, or can be absorbed and reemitted under the form of thermal energy. |
Here we'll have a look at the global radiation budget and its effects on the Earth climate, and focus on the human's impact on that budget, nowadays and in the future. Observations of radiation budget are made with satellites observing Sun and Earth radiations. |
|
Incident energy from the sunLooking globally at the Earth at the top of the atmosphere, the planet's radiation budget must be in equilibrium for the Earth not to become colder or warmer. Although the climate system is in balance, that balance is dynamic, ever-changing.
|
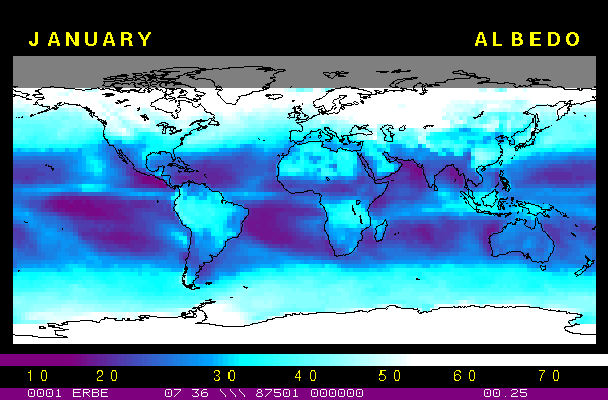
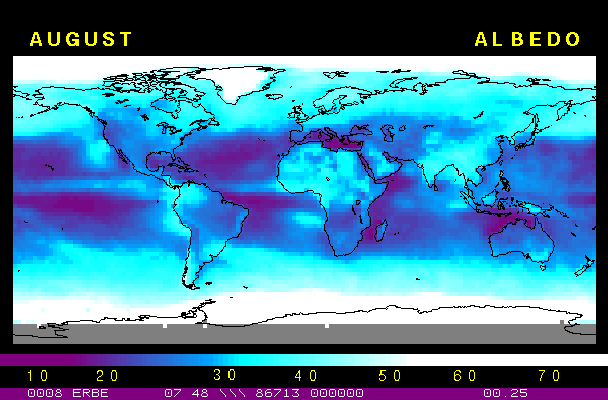
Albedo: energy reflected by the EarthOne part of the solar light striking the Earth is reflected towards space. This fraction of sun light is called albedo. Look at the images 4a and 4b to see the average albedo of our planet in January and August. The global annual average albedo is approximatly 0.30. For example, polar zones exhibit strong albedos because of the high reflectance of the ice.
|
|
|
|
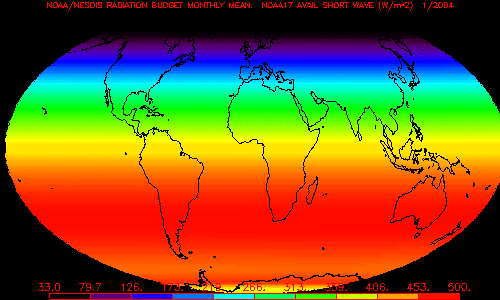
Solar energy wich is not directly reflected (70%, corresponding to around 240 W/m˛) is absorbed by atmosphere and Earth's surface. This process leads to heating of the surface and re-emission of infrared radiations (longwave radiations). One part of these radiations are trapped by the atmospheric gases instead of being re-send to space; this natural greenhouse effect allows our planet's mean temperature to be 15°C. |
|
5. Global annual mean radiative budget in W/m˛. Source: LMD/ Scarab. Click to enlarge (22 K)! |
How can the radiation budget change?Amount of energy receive by the Sun can be different, because for example of the variation of the tilt of the axis of Earth rotation. Contrasts between latitudes and between seasons is larger when obliquity is larger. Climate changes due to astronomic variations are defined by Milankovitch theory.
|
Radiative budget can change:
|
|
|
Radiation balance is a major goal of climate research. 340 W/m˛ of solar flux strike the Earth and the same value is resend to space. The response of Earth's mean temperature to a forcing of 4 W/m2 (the forcing for a doubled atmospheric CO2) would be an increase of about 1 to 4 °C! Calculations must therefore be very accurate. Understanding the complexity of controls and feedbacks and the role of human in the modification of that fragile equilibrium is a key to predict -and prevent!- the future climate.
About this page... |