> English > Climate Encyclopaedia > Food and Climate > basics > 3. Drought in the Mediterranean > * Worksheet 2
> English > Climate Encyclopaedia > Food and Climate > basics > 3. Drought in the Mediterranean > * Worksheet 2
|
|
|
|
Fire has always been a part of the forest ecosystem but today there are more and more forest fires than ever before. If fires are caused by natural factors, forests are able to recover and regrow. The World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF), however, found that 95% of all vegetation fires today are caused by humans.
|
Each year there are more than 50,000 vegetation fires. The WWF has called for preventive measures to avoid fire catastrophes in Southern Europe.
|
After the disastrous vegetation fires in Corsica and on the Côte d'Azur, the increasing dangers of fire in the Mediterranean area have become obvious. Even now between 600,000 and 800,000 hectares of forest become victim to fires every year. This is an area equivalent to the size of Crete.
|
|
|
More than 50,000 fires destroy, on average, 1.5 % of the whole Mediterranean forest area per year. Biodiversity in the Mediterranean has, as a result, diminished. The study by the WWF shows that 95% of fires are caused by humans, either by accident or deliberately. The remaining 5% are caused by natural processes. In countries like Spain, Italy, Portugal and Greece, the number of vegetation fires has quadrupled since the 1960's.
|
|
Aside from human carelessness, other reasons include a change in land use and a massive expansion in the infrastructure needed for mass tourism. Urbanisation has superseded traditional forestry in the Mediterranean area. Arson has become a popular way to convert the areas which were once used for forestry into profitable building land. Longer lasting droughts, low humidity and extreme heat waves mean that fires are easy to start and they spread quickly. As the number of vegetation fires increases, the natural rate at which the Mediterranean ecosystem regenerates has declined.
|
|
In many places a loss of biodiversity, scarceness of water, soil erosion and the formation of desert has been seen. The danger of further vegetation fires rises as a result. Approximately 300,000 square kilometres of European coastlines are endangered. Simple reforestation is not a perfect solution to the problem. So much dry wood accumulates in copses and secondary forests that they are also highly inflammable. To try and reduce forest fires, strict laws and penalties must be enforced. Many of the 50,000 fires each year can be prevented if governments start to spend money on preventative measures rather than simply paying to extinguish fires. Better cooperation between all the institutions involved in fire prevention may prevent many fires (based on a WWF article – source: http://www.wwf.de/presse/pressearchiv/artikel/01349/index.html). The FAO report however states, that "It has been observed, nevertheless, that the heavier the punishments provided by the law, the more difficult it is to prove arson and the more the courts hesitate to condemn arsonists". (http://www.fire.uni-freiburg.de/programmes/un/fao/Wp55_eng.pdf)
Exercise:1. What reasons are there for vegetation fires and what are the consequences of forest fires?2. Many forest fires are caused accidentally. Design a danger sign which points out the danger of forest fires to visitors and shows the best ways to prevent them (cigarettes, fire…)!
|
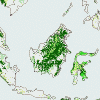
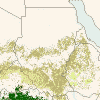
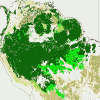
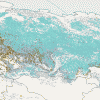
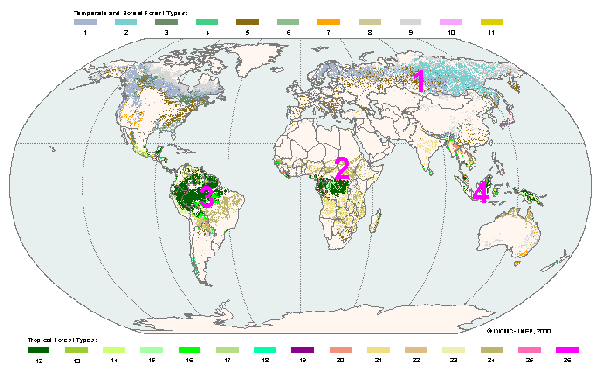
The global viewThe Mediterranean region often makes headlines in Europe because of forest fires. How important are forest fires in Europe on a global scale? Have a look at the world forest map below. Different type of forests are shown in different countries. Click on the thumbnails below to see different regions at a higher resolution (70 kb per image).
|
 |
|
3. The global forest map
|
|
|
4. a-e)Thumbnails:
|
|
Exercise: Fires can be catastrophic to the Mediterranean region. But how important are Mediterranean fires to our global climate? - Compare the numbers on the world map, find out which thumbnail (A, B, C, D) and which of the texts below (a, b, c, d) belongs to which number.
|
About this page:author: Sarah Ancot - University of Nürnberg, Nürnberg, Germany and Dr. Elmar Uherek - Max Planck Institute for Chemistry, Mainz, Germany
|