 > ACCENT en > Nr 7 March 2006 Climate modeling > A: Activities > How will the climate develop?
> ACCENT en > Nr 7 March 2006 Climate modeling > A: Activities > How will the climate develop?
|
Explore a climate modelHow will the climate develop?Test the interactive climate model and answer. Click on the illustrations on this page and enlarge them. It will help you to find the right settings for the model.
|
|
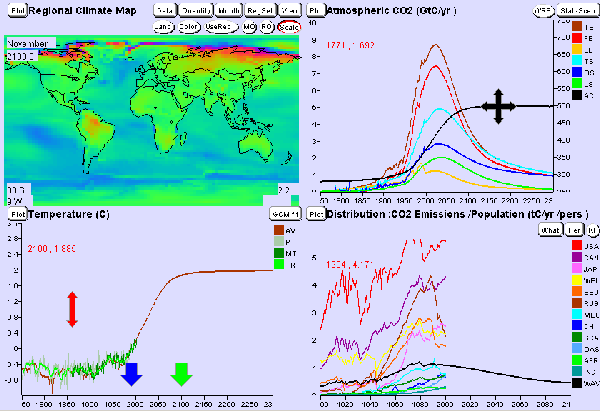
So far we assumed that CO2 will stabilise in the air at 500 ppm (at the moment, in 2006, we have 380 ppm). Is 500 ppm realistic? Now you can start to be a climate modeller. Choose, for example, the following setup: "Regional climate map" at the top left. Please note that the climate changes depend on the months of the year. You can press the "MO" button in order to let the months rotate. At the top right you can choose the atmospheric CO2. The graph gives you information about the stabilisation level (here 500 ppm in 2125) and about the sources (fossil fuel, red; landuse change, orange) and sinks (ocean, blue; biosphere, green). You see now that the world will be on average 1.9 degrees warmer in 2100, but only if we go reduce CO2 emissions immediately. |
 |
|
|
|
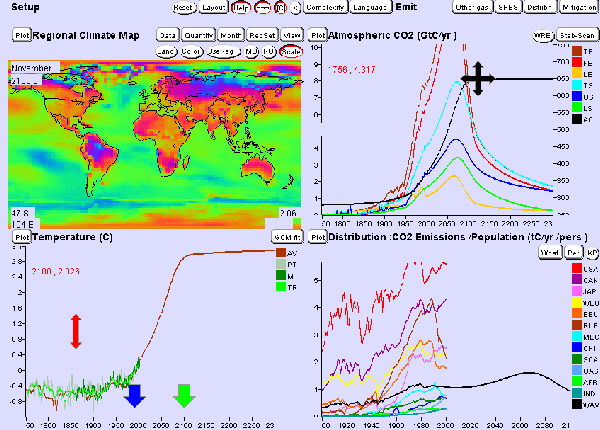
Task 6: 1.9 degrees warming is an average value. Describe: Which regions will become much warmer? Since we still emit more and more CO2 every year climate experts say already now that it will become hard to achieve the limit of 2°C warming, which is regarded as tolerable for the world. Now move the big black cross in the CO2 emissions upwards, for example to 650 ppm and see what happens to our planet. Task 7: What is the average warming now? Which regions are most affected? |
 |
|
|
|
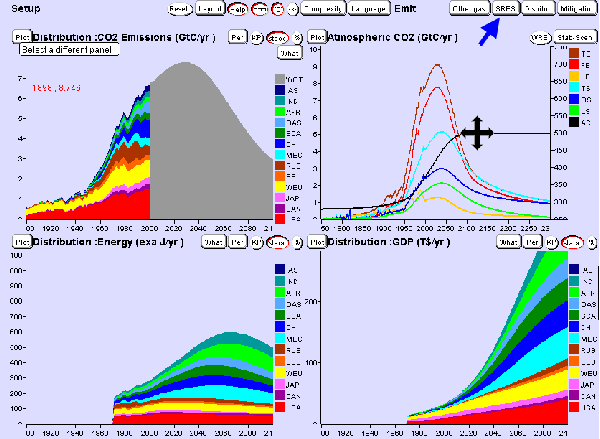
Before you start playing now with other options like precipitation, maximum temperatures and many other tools you have in the regional climate map (button “data”), we need to speak about IPCC scenarios. Task 8: Press reset and choose the distribution of energy usage and the gross national product (GDP). Now choose with the “SRES” button in the upper menu bar different SRES scenarios. Describe the correlation between the three different scenarios and the assumed energy consumption. (4 sentences)
|
 |
|
|
