> English > Climate in brief > - Troposphere
> English > Climate in brief > - Troposphere
|
|
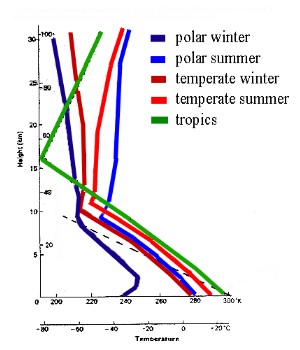
Water vapourIf we define the composition of air, we mean air which contains no water. If we exclude water, air composition is nearly the same all over the world. The amount of water in the air varies greatly and depends strongly on the air temperature. Really cold air is about 0.1% water whereas very warm air can hold much more water, up to 4% of its mass. At the North and South Poles and in the upper troposphere where it is very cold, the air contains less than one gram of water per kilogram of air. In the tropics where it is warm, air contains up to 30 grams of water per kilogram of air. This huge variability makes it extremely difficult to include water in global climate models.
|
|
We have to keep in mind a few rules in order to understand basic processes in the lower atmosphere: 1) Warm air rises. This is why air mixes in the morning when the Sun warms the ground. |
|
As a consequence: Weather (evaporation, cloud formation, rain, snow) and most of the chemical processing of compounds from the oceans, from land and from human activities takes place in the troposphere.
|
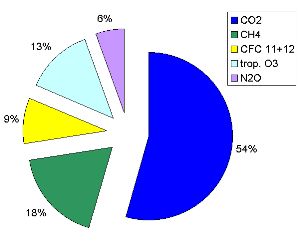
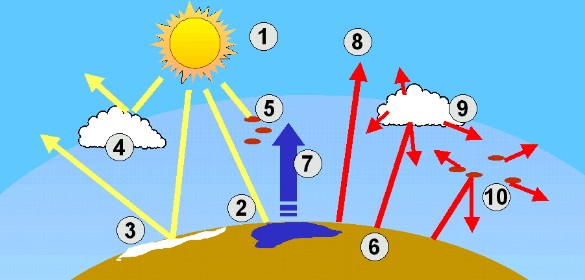
The Greenhouse Effect and global warmingLife on Earth would not be possible without a natural greenhouse effect. Without greenhouse gases, the Earth would be about 33°C cooler and the average temperature would be -18°C instead of 15°C. Water vapour and carbon dioxide are the most important greenhouse gases. Water vapour makes up about 60% of the natural greenhouse effect, and carbon dioxide about 20%. Greenhouse gases trap heat emitted from the Earth and keep it close to the surface. The following image shows what controls the 'central heating' system of our planet.
|
 |
|
4. The world's energy and radiation system
|
|
(1) The Sun is the source of all of the energy reaching the Earth. Which gases act as greenhouse gases and what causes the enhanced greenhouse effect?
|
|
The most important greenhouse gases influenced by humans: - carbon dioxide (CO2) comes mainly from fossil fuel burning.
|
ChemistryMany chemical reactions occur in the troposphere. The chemicals come from many sources including plants, industry, vehicles and the oceans. Nearly all the organic (carbon based) compounds in the troposphere react with one or more of the following species. These are the main atmospheric oxidants and they clean the air of harmful chemicals.
|
Hydroxyl radicals are formed by the action of sunlight and are extremely reactive so don't exist for very long in the atmosphere. Since they react with nearly all other chemicals, they are known as the detergent of the atmosphere. Nitrate radicals are formed in the dark and broken down by sunlight. These, therefore, clean the atmosphere during the night. In order to form these compounds and ozone, three 'ingredients' are necessary: oxygen, sunlight and the nitrogen oxides, nitrous oxide (NO) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2). These two compounds are collectively known as NOx.
|
|
Ozone smogHigh concentrations of ozone can be formed in the troposphere during ozone smog events. Since ozone is harmful to human health and to plants, many studies have been conducted to see how it forms.
|
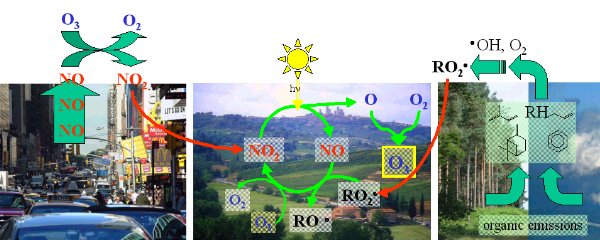 |
|
7. The formation of ozone smog
|
|
Have a look in the topic on the LOWER ATMOSPHERE in the Climate Encyclopaedia for more details on the Greenhouse Effect, on tropospheric ozone and other subjects including vegetation fires.
English proof reading: Lucinda Spokes, UEA Norwich - Sally Taylor, Univ. of Leeds last published: 2005-06-14 |