> English > Climate Encyclopaedia > Upper Atmosphere > more > 2. Ozone
> English > Climate Encyclopaedia > Upper Atmosphere > more > 2. Ozone
|
Upper AtmosphereRead more |
Unit 2:
|
|
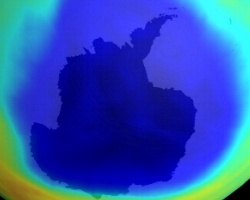
Although ozone has been the subject of research since the 19th Century, it wasn't until the discovery of the Antarctic ozone hole that this research intensified. This unit looks at the history of ozone research, looking primarily at the reactions which lead to ozone depletion. We concentrate on the chlorofluorocarbons (CFC's), since these are the most important ozone destroyers, looking at their characteristics and their modern replacements.
|
We also look at the differing roles of ozone in the stratosphere where it protects us from high intensity ultra-violet radiation from the Sun and in the troposphere where ozone is an important greenhouse gas, contributing to global warming. Scientists assume that the ozone hole will slowly close over the next 50 years. Increasing cooling in the stratosphere may, however, slow down the recovery of the ozone layer. In this unit we investigate what is going on.
|
|