> ENC Master > Climate Encyclopaedia > Upper Atmosphere > more > 2. Ozone
|
|
 |
Higher Atmosphere
Read more |
Unit 2:
Stratospheric ozone, chlorofluorocarbons, the ozone hole and its impacts
|
|
Ozone has already been subject to research in the 19th century, but since the discovery of the Antarctic ozone hole this research has been strongly intensified. A view back shows the history of ozone research. In the following we discuss in detail those reactions which primarily lead to the depletion of ozone. The Chlorofluorocarbons (CFC) are the most important ozone killers. What are their characteristics and how are they replaced nowadays?
|
It is important not to confuse the different roles of ozone in the stratosphere and in the troposphere and, above all, to separate the stratospheric matter from global warming. We explain potential misunderstandings. Scientists assume that the ozone hole will slowly close during the next 50 years. A restraint could be the increasing cooling of the stratosphere. We have a look, what is going on.
|
 |
 |
 |
|
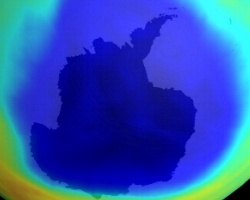
Ozone hole 2003 © NASA GSFC
|
|
About this page:
author: Elmar Uherek - Max Planck Institute for Chemistry, Mainz
last published: 2004-04-20
|
 > ENC Master > Climate Encyclopaedia > Upper Atmosphere > more > 2. Ozone
> ENC Master > Climate Encyclopaedia > Upper Atmosphere > more > 2. Ozone