> ENC Master > Climate Encyclopaedia > Food & Climate > basics > 2. The climate change issue > - contribution of agriculture
> ENC Master > Climate Encyclopaedia > Food & Climate > basics > 2. The climate change issue > - contribution of agriculture
 |
|
|
|
|
|
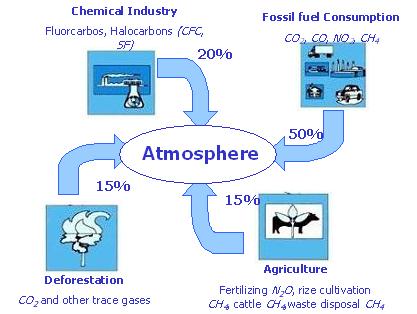
Contribution of agriculture to greenhouse gases.There has been great intensification in agriculture in the last century, nowadays fields are so vast and production is so high, that it is not possible to think about agriculture without the help from machinery and pesticides in most parts of the world.
|
Use of fossil fuelsModern intensive agriculture needs much more energy input than did traditional farming methods, as it relies in the use of machinery for most operations (tillage, harvesting, transport of grains or use of pesticides). 17% of the total energy used in the USA economy is consumed in food systems (6% agricultural production, 6% processing and packaging and 5% for distribution and preparation) this means an annual use of around 1500 litres/person of fuel only for food. |
|
CO2 in soils and forestsBut not only the use of fossil fuels emits greenhouse gases to the atmosphere. The intensive tillage of agricultural land, and deforestation are very effective ways to increase those emissions. Forests are great sinks for CO2. As you know, vegetation needs to absorb CO2 in order to grow (for the photosynthesis process) and trees need a much bigger amount than simple crops, as they have to develop much bigger structures, also forests keep moisture quite high and this helps in the storage function. Then, the cut down of forest areas decreases the possibility of CO2 storaging, not only in the trees but also in all the associated vegetation and the decrease in humidity, also the decomposition of all that organic matter liberates great amounts of CO2. It is said that almost 15% of all the greenhouse gases emissions are produced by forest destruction. The soil is also an important sink, as it keeps a great amount of organic matter that contains Carbon, intensive and aggressive tillage of land under cultivation releases CO2 very fast. When the soil is twisted upside down more Oxygen can get into it and more CO2 can get out f it, as organic matter decomposes more easily and liberates that CO2 (plant litter and living animals) |
Changes in the size of Tropical Forests between 1990 and 1995Annual change (millions of ha) [%] World reduction of forests (Font:FAO 1997) Changes in the size of Tropical Forests between 1990 and 1995. Annual change (millions of ha and %) You might get a better idea of the size changes knowing that 30 millions of ha is aproximately the size of countries like Italy, Poland or Norway.
|
N2O and CH4 from farming wastesNitrous Oxide is produced from a wide variety of biological sources in soil, water and animal wastes. During the last two centuries, human activities have increased N2O concentration by 13%. The main activities producing N2O are fossil fuel combustion, agricultural soil management, industrial sources and the use of N fertilizer, which produces also secondary effects.
|
|
Rice and CH4 productionWhy is rice production such a big source of Methane? This molecule (CH4) is produced by microscopical organisms that live in water (in what is usually called “anaerobic conditions”, as there is a very low concentration of oxygen) As you probably know, rice is one of the major crop productions in the world and it is cultivated in flooded fields, this is the reason why rice fields are large producers of methane Agricultural sources of CH4 account for as much as one third of the total the atmosphere is able to absorb. |
What agriculture can do about GHG emissionsAs we have just seen, agriculture is a large producer of GHG, but this can be changed with a bit of effort. Agriculture can contribute to mitigate GHG emissions by adopting practices that promote capturing of CO2 in soils, crops biomass or trees, which could be the use of less aggressive tillage and the stop of deforestation for more arable land.
|
|
Related pages: More explanations about greenhouse effect: |
Author: Marta Moneo and Ana Iglesias- Universidad Politécnica de Madrid - España |