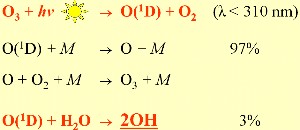> ENC Master > Climate Encyclopaedia > Lower Atmosphere > more > 3. Ozone & fire > - ozone reactions
> ENC Master > Climate Encyclopaedia > Lower Atmosphere > more > 3. Ozone & fire > - ozone reactions
 |
|
|
|
Lower AtmosphereRead more |
Why is ozone dangerous?In the topic higher atmosphere we understand, that ozone is essential in the stratosphere in order to protect us from the damage of ultraviolett light. In our surrounding next to the Earth surface however, we do not want to have it. But what sort of harm does ozone do?
|
|
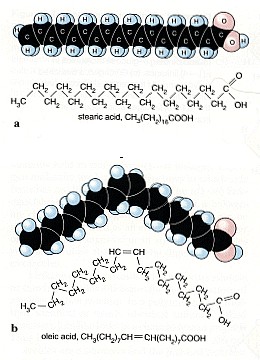
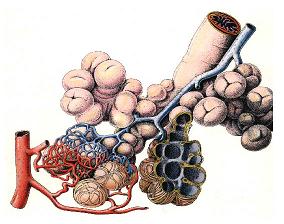
Ozone attacks our respiratory systemAfter our first year in organic chemistry we know: Carbon C and hydrogen H are present everywhere in living organisms, in plants, in animals and also in our body. Besides from C and H there may also be oxygen O, nitrogen N, sulphur S and phosphor P in organic compounds, but hydrocarbons form the backbone. This backbone includes C-C single bonds, which are very strong and C=C double bonds, which are in some way easier to attack. For ozone in particular the double bonds are interesting. We find them everywhere: in unsaturated fatty acids, haemoglobin, proteins and many other bio-molecules, also on the surface of the pulmonary alveoli in our lungs and its mucous membrane. The other two main oxidants, OH and NO3 have an extremely short lifetime and react immediately when they are formed. Ozone however finds its way down to the lungs. Every day 20,000 liters of air pass the tiny alveoli, which have a total surface of 80-100 square-meters. Ozone can penetrate and react.
|
Ozone cracks double bonds.Ozone reacts e.g. with fatty acids in the lungs in the same way than in the air. It adds to the double bonds, cracks it and aggressive radicals are formed which lead to further oxidation. The consequence is an inflammation of the lungs, which is in particular dangerous for people with asthma, but also for healthy people. You will experience a decreasing lung capacity and a shallow breathing during exercise. Never do sports or hard work if ozone levels are high!
|
|
 |
|
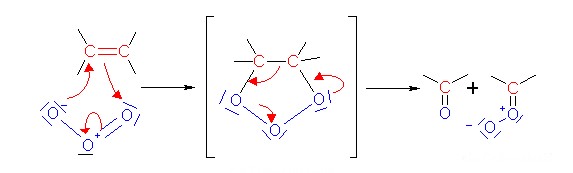
4. The reaction of ozone with double bonds (ozonolysis) leads to a cracking of the bond.
|
|
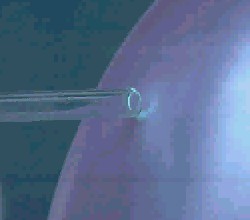
Ozone does not only crack double bonds in our lungs, it also attacks double bonds of terpenes, the smelling bio-molecules in the forest, and many other molecules in the air. If you expose leafs to larger ozone concentrations, they are damaged as well. With very high concentrations you can even cut the double bonds in the rubber of an air balloon and make it burst.
|
|
|
|
Related pages: You find basic information about ozone and what harm it does on leaves at:
|
About this page:author: Dr. Elmar Uherek - Max Planck Institute for Chemistry Mainz
|