> English > Climate Encyclopaedia > Lower Atmosphere > basics > 3. Ozone and nitrogen oxides > - nitrogen oxides
> English > Climate Encyclopaedia > Lower Atmosphere > basics > 3. Ozone and nitrogen oxides > - nitrogen oxides
|
Lower AtmosphereBasics |
Nitrogen oxides - formation and relevanceNitrogen oxides play an important role in the chemistry of our atmosphere. In this section we look at how they are formed and why they are so important.
|
 |
|
|
1. Traffic, an important source of nitrogen oxides. (c) FreeFoto.com |
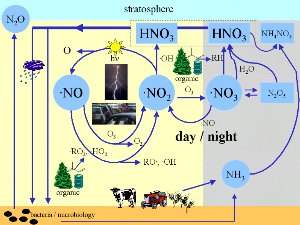
Where do nitrogen oxides come from?The most important forms of reactive nitrogen in the air are nitrogen monoxide (NO) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2) and together we call them NOx. Nitrogen oxides are formed in the atmosphere mainly from the breakdown of nitrogen gas (N2). Because the two nitrogen atoms in N2 are bound very strongly together (with a nitrogen to nitrogen triple bond), it isn't easy to break N2 down into its atoms. A few bacteria have developed special mechanisms to do this and very high temperatures can also break the molecule down. Vehicle engines operate at high enough temperatures and nitrogen oxides are emitted in the exhaust fumes. Catalytic converters fitted to cars decrease the production of these harmful compounds. Nitrogen oxides can also be formed when biomass is burnt and during lightning. 2. right: Lightning is another important source of nitrogen oxides. Picture by Bernhard Mühr / Karlsruher Wolkenatlas.
|
|
|
Names of nitrogen compounds:
|
|
Nitrogen oxides are very important in the formation and loss of tropospheric ozone. They are involved in catalytic cycles and continuously react and reform. Nitrogen dioxide (NO2) is broken down by sunlight to form nitrogen monoxide (NO). This NO then re-reacts to form more NO2. Ozone and unstable oxygen compounds known as peroxy-radicals can also be involved in this cycle. We will look at these reactions in more detail later. We emit far too much of these nitrogen oxides during combustion proceses, particularly from vehicles. The main aim of fitting catalytic converters to cars is to reduce the emission of these compounds into the air. Other important nitrogen gases in the atmosphere include: Ammonia (NH3) is the most important basic gas in the atmosphere. It comes mainly from agriculture, both from the storage of animal wastes and from fertiliser use. It reacts in the atmosphere with acid species like nitric acid to form aerosol particles.
|
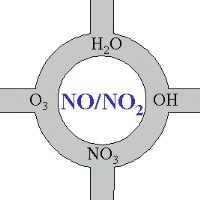
Nitrogen oxides - at the centre of atmospheric chemistryNitrogen oxides are really at the centre of atmospheric chemistry. Most chemical compounds which are oxidised and removed from the air or are transformed into other chemical species come into touch directly or indirectly with NO or NO2.
|
|
|
Related pages Nitrate radicals have a special role in night-time chemistry. Find out more at: More information about the link between nitrogen oxides and the ozone hole can be found at: We learn more about the nitrogen cycle and its relation to ozone in the About this page:author: Dr. Elmar Uherek - Max Planck Institute for Chemstry, Mainz, Germany
|