> ACCENT en > Nr 3 Sept. 2005 methane/energy > C: Renewable Energies
> ACCENT en > Nr 3 Sept. 2005 methane/energy > C: Renewable Energies
|
Context: Energy today and tomorrowWhat are the alternatives?
|
Nuclear powerNuclear power, although relatively cheap, is not an unlimited resource. Resources of uranium will last for about 40 years if there is not any reprocessing. Reprocessing and world-wide expansion of nuclear power means that plutonium, which can also be used in nuclear weapons, has to be traded. This is potentially dangerous in a world of international terrorism and unstable regions.
Renewable Energies
|
|
 |
|
2. Oil seed rape - Can we replace fossil fuels by renewables? © freefoto.com
|
|
Hydro powerHydro power makes already up 17% of the globally produced electricity (about 2% of the global primary energy demand). This is more than all other renewable resources together. Hydro power can also compete in price. But at most of the places where it can be used without destroying nature and landscape too much, it is already used. Therefore, with increasing energy demand, the relative share of hydro power cannot increase significantly.
|
Solar energy groupPhotovoltaicsPhotovoltaics transform solar energy by means of semi-conductors. It is probably the technology with the highest potential, but also with the highest development needs and the highest price at the moment. Electricity generation based on photovoltaics costs between 0.5 and 0.75 EUR per kWh compared to less than 0.05 EUR for fossil fuel driven power plants. Moreover the production of solar cells is costly and energy intensive. |
|
|
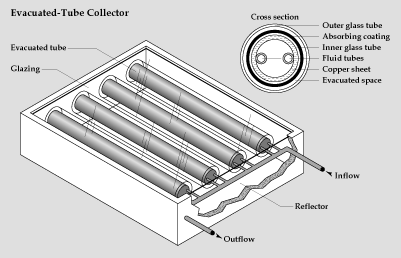
They have to work for 3-5 years in order to bring in the energy which was needed to produce them. Further improvements are needed in order to make this technology competitive for large scale power generation. Solar thermal energyA more competitive technology is solar thermal energy. Here, solar energy is focussed with the help of mirrors or glass tubes onto an absorber, for example water, heating it up . The conversion into electricity can be only efficient in larger power plants (in contrast to photovoltaics). |
|
|
One variant is the solar thermal tower technology, where heat is collected under a massive flat greenhouse and let out through a very high updraft chimney which contains a turbine. |
|
BiomassWood, sugar cane, sunflower and rape seed oil and gas from bio-waste are typical biological products used for energy production. After processing they can be used for electricity generation or heating. |
|
Only cheap wood can be used in a competitive way for energy production and resources are limited. Biogas from agronomy, landfills and sewage plants has higher potentials. Rape seed or sunflower oil is in some cases an alternative for fossil oil and can be used as biodiesel. Bio-ethanol from sugar cane or cereals can be blended with fuel for cars or replace it completely in special engines. |
|
However, the growing and combustion processes are not free of secondary effects (fertilizers, exhaust gases), which can have negative impacts on ozone layer depletion (N2O emissions), eutrophication (NOx and NH3 emission) and acidification of soils.
|
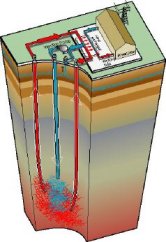
Geothermal heatTemperature increases the deeper you go into the Earth (about 3°C per 100 m in Europe). This heat can be transported to the Earth's surface for example by water as a carrier and heat exchanger.
10.On the right: Geothermal heat can be accessed by drilling holes in the Earth and pumping water through as a heat exchanger.
|
|
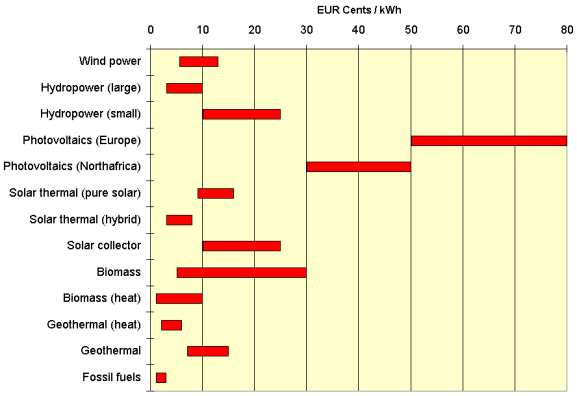
Electricity-generating costsA big disadvantage of renewable energies is that they are still significantly more expensive than traditional fossil fuel. The following chart gives an overview of electricity generating costs and in two cases also of heat generating costs for different renewable energies compared to fossil fuels. |
 |
|
11. Electricity-generating costs for different renewable energies compared to fossil fuels. The fossil fuel costs do not include indirect costs for the compensation of environmental damage.The content of this website is based on several Internet publications of the International Energy Agency IEA and a brochure "Renewable Energies" (2004) of the German ministry of the environment.
|