> ENC Master > Climate Encyclopaedia > Climate in Cities > more > 1. Air Pollution > - Impact
> ENC Master > Climate Encyclopaedia > Climate in Cities > more > 1. Air Pollution > - Impact
 |
|
|
|
Urban ClimateRead more |
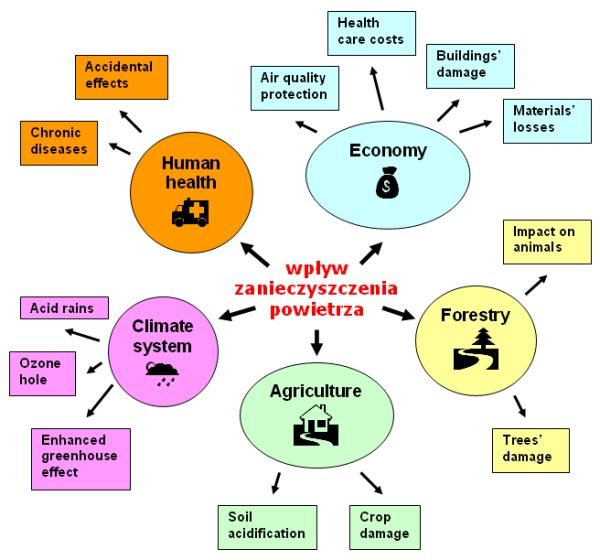
Impact of air pollution (overview)Air pollution may be dangerous for human health, but it also has negative impact on natural environment's functioning. Additionally, it causes economic losses. Meteorological conditions modify to a large extent the effects of air pollution. |
|
Air pollution causes numerous diseases and can threaten human health and life. Air pollution usually acts gradually, in small doses, causing chronic problems with health. However, in some cases (as described in part "Urban bioclimate") they may cause even a sudden death. In the case of plants and agriculture, air pollution decreases harvests and causes acidification of the soil. In the case of forests, air pollution causes their decreased productivity and direct damage of trees. As far as global climate change is concerned, the effects of air pollution on water and plant ecosystems are the most important ones, as they influence the assimilation of CO2, one of the basic process of atmosphere-biosphere-hydrosphere gas exchange.
|
 |
|
1. Air pollution impact
|
|
Air pollution generates various economic losses but their detailed estimation is extremely difficult. They may be divided into four groups:
|
|
There is a close connection between air pollution and meteorological conditions. Main role is played by the wind which may cause fast dispersion of the pollution, but also decrease its local concentration. Transporting the pollution on large distances may cause their negative impact on ecosystems placed far away from the emission source (e.g. Siberian or Canadian taiga). On the other hand, air stagnation and temperature inversion may be dangerous when they occur in the vicinity of emission source as they unable the pollution dispersion. If a source of emission (e.g. the top of a chimney) is placed below the inversion range, the pollution does not disperse, its concentration increases and may exceed the allowed levels. In the moderate climate, the inversion occurs not only in the mountain valleys but also in the lowlands. During the inversion duration, the water vapour may reach the temperature below the condensation point. Then the fog forms which complicates the situation even more, as it contributes to the origin of the smog. It does not allow the light to come through it and therefore the ground and lower layers of the air may not be warmed, so the inversion continues. Moreover, smog contains high, dangerous concentrations of various pollutants, which caused many times intoxication and even death of many persons in large cities.
|
|
Related pages: Learn more about impact of air pollution to human health in: |
|
About this page:Authors: Pawel Jezioro, Anita Bokwa - Jagiellonian University - Cracow / Poland |