
> ACCENT en > No 1 May 2005 vegetation/CO2
VEGETATION around us
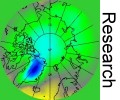
Forests and the fever chart of carbon dioxide
|
 |
 |
Observation of trace gases and carbon dioxide
Some gases in our atmosphere appear only close to their sources. Scents from trees have to be observed in the forest. Others like carbon dioxide spread nearly homogeneously round the globe and can be observed at many places. One measurement station is Mace Head. What do scientists do there? |
 | | Plant life as part of an atmospheric surrounding
Plant life is influenced by the atmospheric composition, the atmospheric composition is determined by plant life. Carbon dioxide needed in photosynthesis is a prominent example. What are the interactions?
|
 | | Activities
Do you know where the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide in our atmosphere comes from and where it goes? Think about the role of plants and how to measure their influence.
|
 | | Links
More information in the Internet about:
- emissions from trees and other plants, carbon dioxide and the carbon cycle
|
 | | Information for Teachers
Draft solutions, download material and more detailed information in the Material Area for teachers.
|
 > ACCENT en > No 1 May 2005 vegetation/CO2
> ACCENT en > No 1 May 2005 vegetation/CO2 > ACCENT en > No 1 May 2005 vegetation/CO2
> ACCENT en > No 1 May 2005 vegetation/CO2