|
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
| |
|
|
 |
The Oceans
Read more |
2. Oceanic nutrients - more
Worksheet 2: Phytoplankton and CO2 absorption
|
|
|
|
|
 |
1. Absorption of carbon dioxide (CO2)
Plants take up carbon dioxide in order to grow. The CO2 provides the carbon atoms needed to make up the organic compounds in the cells of the plants. This process is known as photosynthesis, it needs energy from the Sun and is carried out by chlorophyll in plant cells. Chlorophyll is the pigment which makes plants green.
As a result of photosynthesis, plants take up carbon dioxide and so remove this important greenhouse gas from the air. We know that trees take up a lot of CO2 from the air but the tiny phytoplankton in the oceans are also a very important CO2 sink both because there are so many of them and because they grow so quickly.
Phytoplankton are not only involved in regulation of carbon dioxide in the air but they also release other gases into the atmosphere which affect our climate.
|
 |
 |
|
1. Parks act as oxygen producers (source: Hemera, Big Box of Art)
|
Exercise 1: The importance of phytoplankton and dust to our climate
Fill in the missing words.
|
 |
 |
|
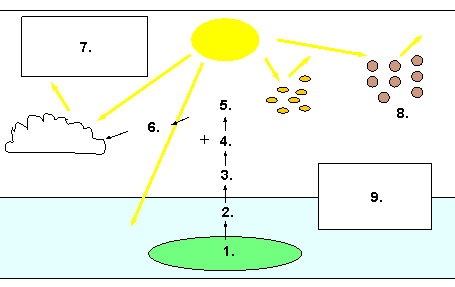
2. The role of phytoplankton and dust in our climate.
Illustration by Lucinda Spokes, modified by Julia Heres.
|
|
1. ___________________
2. ___________________
3. ___________________
4. ___________________
5. ___________________
6. ___________________
7. ___________________
8. ___________________
9. ___________________
|
 |
Missing words:
- dust particles
- sulphate aerosols
- DMS
- phytoplankton
- CCN
- cooling - indirect light scattering by clouds
- cooling - direct light scattering by aerosols
- DMS
- iron
|
|
We know that phytoplankton not only need sunlight and carbon dioxide to grow but also need other nutrients. The most important nutrients are nitrogen and phosphorous. Phytoplankton generally grow until one of these nutrients is used up and then they stop growing. In some areas of the ocean, however, there is plenty of nitrogen and phosphorous but phytoplankton don't grow well.
Exercise 2: The scientist, John Martin, once said "Give me a tanker load of iron and I'll give you the next Ice Age". What did he mean by this?
|
Exercise 3: How do phytoplankon affect our climate?
Fill in the gaps with the right words.
The growth of ________________________ in the oceans is important to our climate. Using energy from the Sun, these single celled plants take up ______________________ from the air during ___________________________. During this process ____________________ and glucose are formed. This glucose then reacts to form organic compounds which make up the cells.
Some phytoplankton species produce the _____________________ containing gas _______________________. Once in the air, this gas can react with iron to form _________________ aerosols.
These aerosols _____________ reflect sunlight back into space and this causes a cooling of the Earth. They also can act as __________________________________ allowing clouds to form. Clouds have an ______________ effect on climate. Some types of cloud reflect sunlight back into space and therefore cause _______________. Others trap heat from the surface of the Earth enhancing the ____________________________ and cause ________________.
In some regions of the oceans nutrients such as _____________________________ are available in sufficient amounts for the growth of phytoplankton. But the _________ of iron can prevent phytoplankton growing in some ocean areas.
If phytoplankton growth is increased in the ocean, more ___________________________ will be removed from the air. When these phytoplankton die or are eaten, they sink to the ocean floor taking their carbon with them. Some people suggest that adding _____________ to parts of the ocean may help reduce __________________________ .
|
 |
 |
|
3. Cartoon from Hemera.
Big box of art.
|
|
 |
Missing words:
lack, greenhouse effect, phytoplankton, cloud condensation nuclei, iron, sulphur, cooling, photosynthesis, indirect, sulphate, global warming, carbon dioxide, dimethyl sulphide, oxygen, nitrate and phosphate, carbon dioxide, directly, warming.
|
Exercise 4:
Read the text again and then answer these questions:
Click the GREEN button, if you think that the answer is correct and the RED button, if you think that the statement is wrong.
|
a) Rising concentrations of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere increases global warming.
|
 |
|
b) Emissions of carbon dioxide decrease global warming.
|
 |
|
c) Forests are huge carbon stores. Planting trees reduces the amount of CO2 in the air.
|
 |
|
d) Adding iron to the sea prevents phytoplankton growing.
|
 |
|
e) When phytoplankton die, some of them sink to the bottom of the ocean. This process removes helps remove carbon dioxide from the air.
|
 |
|
f) The ecology of the sea is not affected by the addition of iron.
|
 |
|
g) Adding iron to the sea to remove carbon dioxide may actually result in the production of stronger greenhouse gases such as methane.
|
 |
|
About this page:
author: Bernd Wohlhöfer - University of Nürnberg, Nürnberg, Germany
scientific reviewing: Dr. Lucinda Spokes - School of Environmental Sciences, University of East Anglia, Norwich, U.K.
educational reviewing: Prof. Dr. Helmut Schrettenbrunner, Dr.Yvonne Schleicher and Julia Heres - University of Nürnberg, Nürnberg, Germany
last update: 2004-11-18
|
|
 |
|







