El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO)
The Southern Ocean Oscillation is made up of two phases, El Niño and La Niña, and has affected climate for many centuries, primarily in the Southern Hemisphere. Recent research shows that it may also have some impact on the climate of the Northern Hemisphere.
Different temperature and rainfall conditions are seen during El Niño and La Niña events, not only in the Tropical Pacific but also in distant regions of the world including the Northern latitudes. These variations can sometimes bring about extraordinary episodes of dangerous floods and droughts.
During El Niño events, temperatures in the East Pacific increase along with evaporation rates and rainfall amounts, while lower than average rainfall amounts are seen on the West side of the Ocean. The opposite conditions are seen during the La Niña phase.
|
 |
 |
 |
|
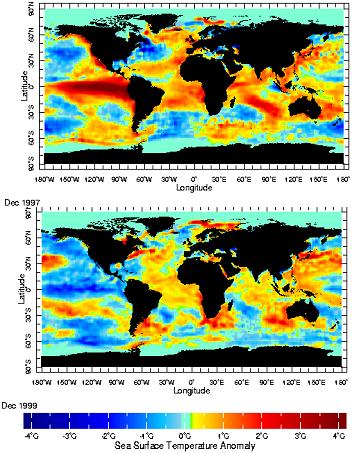
1. Sea surface temperature anomalies during El niño and La Niña episodes. Source: NOAA NCEP EMC CMB GLOBAL monthly Sea Surface Temperature Anomaly Dec 1997 and Dec 1999) (degree Celsius).
These two maps show the differences in surface ocean temperatures during El Niño episodes (top picture) and La Niña episodes (bottom picture).
|
|







