|
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
| |
|
|
 |
How are
people changing
the climate?
Basics |
|
Unit 2:
What will
a warmer world be like?
A warmer global climate will definitely mean more than just more sweat! It may, for example, change wind and rain patterns and it may lead to rising sea levels. These changes will affect plant and animal life as well as human health – not to mention our homes, agriculture, businesses and economies.
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Climate change
The future climate will be determined partly by how much greenhouse gases we emit, which is in turn determined by future population size, fossil fuel consumption, etc. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) (read more about IPCC here) has identified how much we can expect the climate to change (read more about future emissions here). If nothing we do not take action to limit emissions of greenhouse gases, the IPCC says that by 2100 we can expect:
|
 |
 |
|
1. Thunder and lightning: Climate change may lead to more extreme weather, such as more frequent thunderstorms. Photo: The NOAA Photo Library (click to enlarge, 48 kB)
|
|
 |
- the mean surface temperature to increase by 1.4–5.8 °C compared to 1990
- the sea-level to rise between 9 and 88 cm
- 5–20% more rain and snow
- more extreme weather, such as cloudbursts and heat waves, which in turn will cause flooding, landslides, drought, and forest fires, and
- wind and ocean currents to change direction, which can cause local climate changes.
Find out more about
IPCC's future scenarios here.
|
|
The reason that scientists do not know whether the temperature will increase by a little more than one degree or up to six degrees is that, first, they do not know how much we will emit in the future, and second, it is still uncertain how sensitive the climate on Earth is to emissions of greenhouse gases.
Moreover, the above figures are averages for the entire planet. This means that some places may become much warmer, while others may change little, or even become cooler. But the degree of climate change a particular country faces has little to do with how much it has emitted. Greenhouse gases are well mixed with the other gases in the air. After they are emitted, they do not stay in the same place, but rather spread out throughout the atmosphere. Once they are there, they stay a long time. This is why it is not true that the biggest emitters will suffer the biggest climate changes. The most serious consequences of an increased greenhouse effect are just as likely to show up in places far away from where the emissions originated.
What are the consequences of global warming?
The impacts of global warming will vary from place to place. The weather can be drier or wetter, warmer or colder, or more or less windy. Europe will generally become warmer, particularly in the winter. In Northern, Eastern, and Central Europe, increased rainfall and heavier showers will make flooding a bigger problem, at the same time as we can expect more frequent drought in the southern parts of the continent because of less rainfall and more evaporation. The maps show how the climate may change in Europe.
|
 |
 |
|
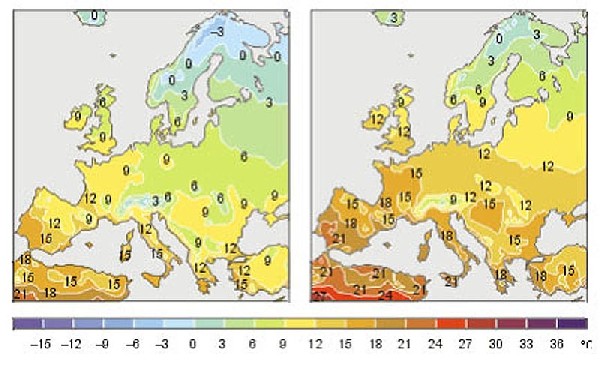
2. HOTTER ALL OVER: How temperatures could change in Europe during this century because of global warming. The left map shows mean temperatures throughout the year, measured with thermometers, during the period 1961-1990. The right map shows what the mean temperatures could be during the years 2071-2100, according to one climate model. The numbers are uncertain and another model might get somewhat different results. Also, the results depend on how much greenhouse gases will be emitted to the atmosphere. Source: Sweclim/Naturvardsverket http://www.naturvardsverket.se/index.php3?main=/dokument/fororen/klimat/klimat/varmare.html (click to enlarge, 79 kB)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
|
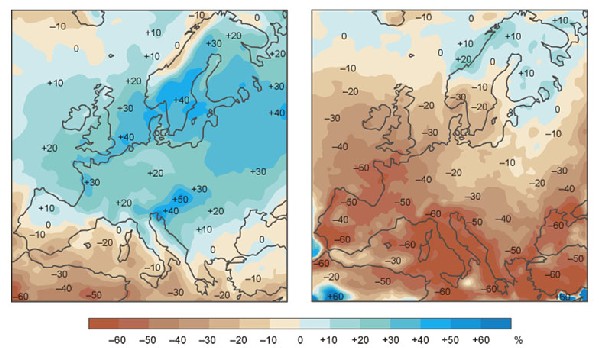
3. BOTH WET AND DRY: How precipitation (rain and snow) could change in Europe during this century because of global warming. The left map shows changes in winter precipitation. The right map shows changes in summer precipitation. These maps are made by a climate model. The numbers are uncertain and another model might get somewhat different results. Also, the results depend on how much greenhouse gases will be emitted to the atmosphere. Source: Sweclim/Naturvardsverket http://www.naturvardsverket.se/index.php3?main=/dokument/fororen/klimat/klimat/varmare.html (click to enlarge, 65 kB)
|
|
Animals and plants must find new places to live
Changes in climate also affect the living conditions of animals and plants – both for individual species and for entire ecosystems. Many species will not thrive if their habitats become drier, colder, wetter, or warmer. Some will migrate to new habitats, others may die out. The most vulnerable species are those that are specially adapted to particular areas. A warmer climate will cause species and ecosystems to move towards the poles and up the mountains. Species that already live in northern or alpine regions are particularly vulnerable, since their habitats will be encroached upon and they will have no place to go: species that live in the mountains cannot move higher up once they reach the top. In the polar regions, the sea ice will melt earlier in the spring and form later in the fall, with serious consequences for species that live on or around the sea ice (for example, the polar bear and some seal species).
|
 |
 |
|
4. HIGHER GROUND: When the climate is warming, mountain-living species move to higher ground. This is a North American mountain goat (Oreamnos americanus)
|
|
 |
Observations have shown that the warming over the last 30 years has already affected animal and plant life in Europe. For example, some bird and butterfly species have expanded their habitats; a study of the spring growth of several plant species shows that budding and flowering started 2–5 days earlier per decade over the last 50 years; the spring migration of birds and egg laying has started 2–5 days earlier for each decade; and species that are specially adapted to a particular climate have moved an average of 6 km toward the poles, or 6 meters higher in altitude, per decade.
A crucial factor for how animal and plant life will survive is how fast the warming actually occurs – since the longer time they have to adapt, the greater the chance that they will be successful. Rapid global warming and sudden climate changes give the species less time than if the changes occur slowly and gradually.
|
Next page
|
 |
 |
 |
|
5. THINNER BEARS: The polar bear is threatened by climate change. It specializes in catching seal on the edges of the sea ice around the North Pole, and shorter seasons with ice cover will give the polar bear a shorter hunting season. Studies show that polar bears have a lower body weight than before. Photo: NOAA Photo Library (click to enlarge, 49 kB).
|
|
About this page:
Author: Camilla Schreiner - CICERO (Centre for International Climate and Environmental Research - Oslo) - Norway.
Scientific reviewers: Andreas Tjernshaugen - CICERO, Norway - 2004-01-20 and Dr. Knut Alfsen - Statistics Norway, Norway - 2003-09-12.
Educational reviewer: Nina Arnesen - Marienlyst School, Oslo, Norway - 2004-03-10.
Last update: 2004-03-27.
|
|
 |
|







