|
|
 |
Exercise: Right or wrong?
Can you answer the following questions on the North Atlantic Oscillation?
Click the green button, if you think the answer is correct
and the red button, if you think it's wrong.
|
The North Atlantic Oscillation (NAO) is a result of pressure differences between the Azores (30° N) and Iceland at 60°N.
|
 |
|
The North Atlantic Oscillation (NAO) is a result of temperature differences between the Azores (30° N) and Iceland at 60°N.
|
 |
|
The North Atlantic Oscillation (NAO) is a result of precipitation between the Azores (30° N) and Iceland at 60° N.
|
 |
|
The North Atlantic Oscillation (NAO) is most important in summer.
|
 |
|
The North Atlantic Oscillation (NAO) is most important in spring and autumn.
|
 |
|
The North Atlantic Oscillation (NAO) is most important in winter.
|
 |
|
The North Atlantic Oscillation (NAO) has only one phase.
|
 |
|
The North Atlantic Oscillation (NAO) has two phases.
|
 |
|
Can you fill the gaps?
The North Atlantic Oscillation (NAO) is a result of
.differences between the
at 30° N and
.. at 60°N.
The NAO is most improtant in
.and has
phases. Each causes distinct weather conditions around the North Atlantic.
..,
.,
and
are all directly affected by the phase of the NAO.
Missing words:
Agricultural harvests, Azores, engery supply, fisheries, Iceland, pressure, two, water management, winter.
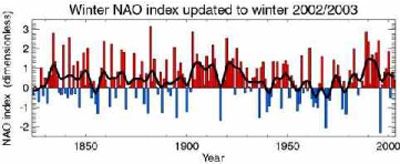
Try to describe and interpret the Winter NAO index (1800-2000)!
|
 |
 |
|
Winter NAO index, updated to winter 2002/2003, image courtesy: Dr. Tim Osborn at the Climatic Research Unit, University of East Anglia, Norwich, U.K.
|
|
 |
................................
................................
................................
................................ |
|
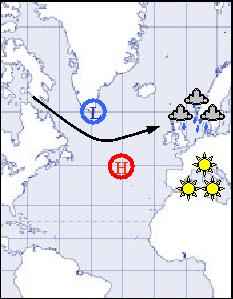
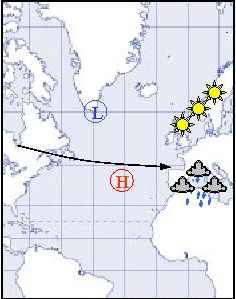
Positive and negative NAO conditions
Have a look at the two pictures and write down what you have learnt
about air-pressure, storms, winds, warm and wet winters, cold and dry winters, etc.. |
|
This picture shows positive NAO conditions. |
 |
This picture shows negative NAO conditions.
|
 |
 |
positive NAO conditions
image source: see chapter 1, Oceans and Climate, text "North Atlantic Oscillation" |
|
 |
 |
 |
negative NAO conditions |
|
 |
 |
|
Clipart, courtesy: Hemera - Big box of art
|
|
 |
|
About this page:
- Author: - Dr. Schleicher - University of Nürnberg - Germany
- scientific reviewing:
- educational reviewing: Dr. Schrettenbrunner / J. Heres
- last update: 29.10.03
|
|
 |
|









