|
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
| |
|
|
 |
Lower Atmosphere
Read more |
Worksheet 1
Ozone and its chemical properties
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
T 1 |
Find the second resonance structure of the ozone molecule below. |
|
|
|
T 2 |
Explain why the O3 molecule has dipole character and compare it with a CO2 molecule and a H2O molecule. |
|
T 3 |
If ozone reacts with an alkene (ozonolysis) the alkene molecule is cracked at the C=C double bond. As products 2 carbonyl compounds are formed in several reaction steps. Write down and name the products of the ozonolysis of
a) 2-butene and
b) 2-methyl-2-butene |
Some properties of ozone:
|
|
|
l T b = -112.5° C |
l badly water-soluble |
|
l T m = -251.4° C |
l soluble i.e. in CF2Cl2 |
|
l µ = 0.49 D |
l toxic |
|
l bluish color |
l O2/O3 (w (O3) < 10% stabel below 100° C |
|
l characteristic smell |
l O3(l), O3(s) explode during contact |
strong oxidizing agent:
|
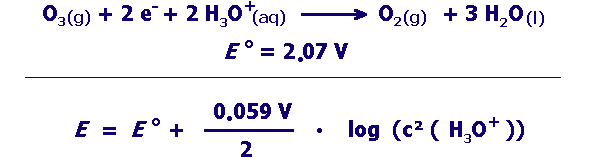 |
 |
|
examples of oxidation reactions with ozone
|
|
|
T 4 |
Can the oxidation with ozone proceed better at high or low pH? Give reasons for your answer using the suitable pieces of information in the box above. |
|
T 5 |
Iodide ions can also be oxidized by molecular chlorine. Write down the reaction scheme and explain the difference to reaction no.1 from the box above. |
|
T6 |
In atmospheric cloud droplets ozone oxidises sulfurous acid (sulfur dioxide in water). This oxidation better takes place at high pH levels.
- Discuss this research result.
- Refer to your results of task No.: T4.
|
|
About this page:
Authors: M. Seesing, M. Tausch - Universität Duisburg-Essen, Duisburg / Germany
Scientific reviewer: Dr. Rolf Sander - Max Planck Institute for Chemistry, Mainz - 2004-05-18
Last update: 2004-06-07
|
|
 |
|









